|
II. Urban Land
Use
A. Land Rent and Manufacturing Land
1. Price of land
a. Definitions
- Land rent - periodic payment by a
land user to a land owner
- Market value - amount paid to become
the land owner
PV = R / i
.
.
.
.
- Land rent is considered to be
"price" of land
.
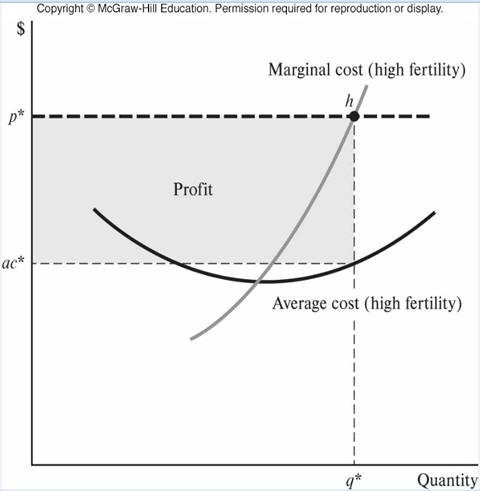
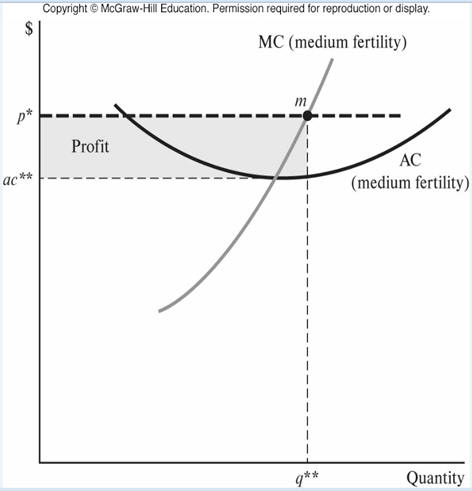
b. Agricultural rent
- David Ricardo - price of agricultural land
based on fertility (productivity)
.
.
- Leftover principle - competition
among farmers for land leads to landlords getting the leftovers
(excess of total revenue over nonland costs)
.
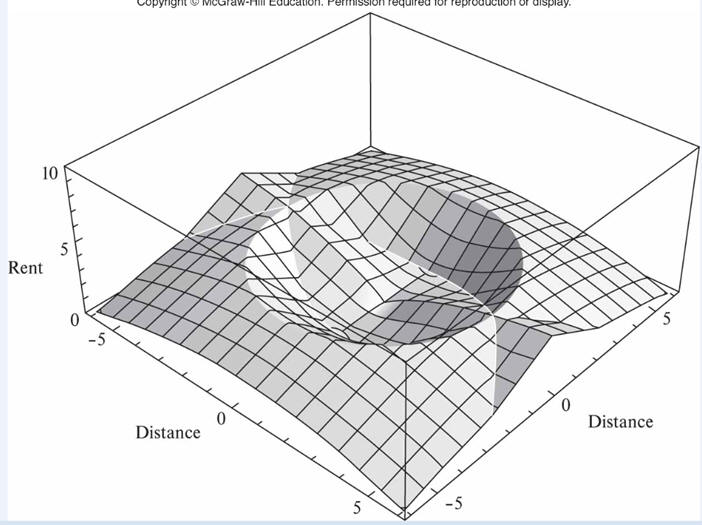
2. Manufacturing sector
- Accessibility to export transportation more
important than fertility
.
a. Freight vs. labor costs
-
Assume inputs and outputs go through a
central freight terminal
-
Inputs shipped from central freight
terminal to manufacturing facility and vice versa for outputs
-
Labor must be compensated for longer
commuting costs
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
b. Impact of
intracity truck
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
c. Impact of
intercity truck and beltways
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
|


