D. Consumer Cities and Central Places
- Look at the impact of consumer decisions
.
1. Monopolistic competition in
location
a. Assumptions
(1) Product differentiation
.
(2) No artificial barriers to entry
.
b. Short-run and long-run equilibrium
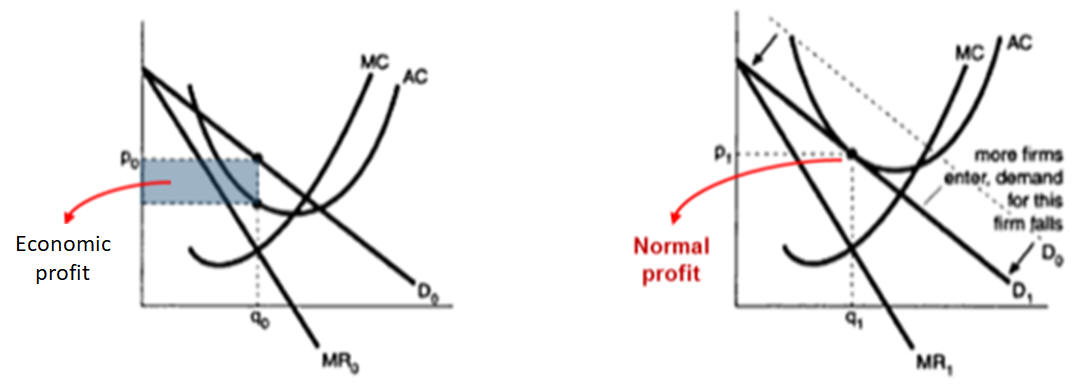
c. Spatial context
.
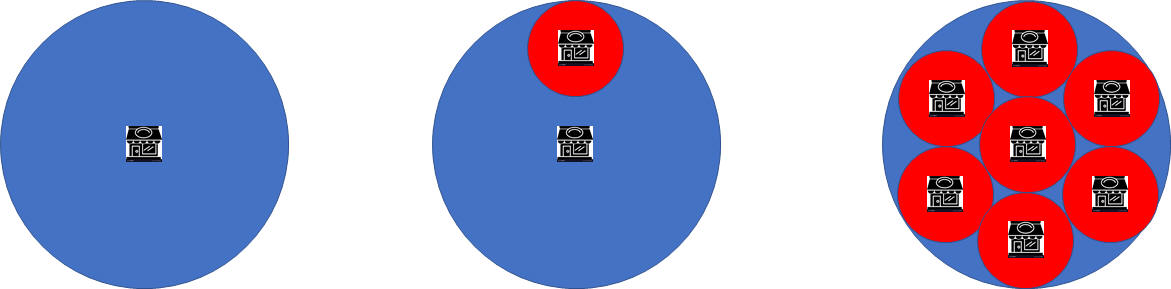
.
2. Market areas
a. Market size
d (p) = per capita demand
N = city population
.
Ex. -
Restaurants
.
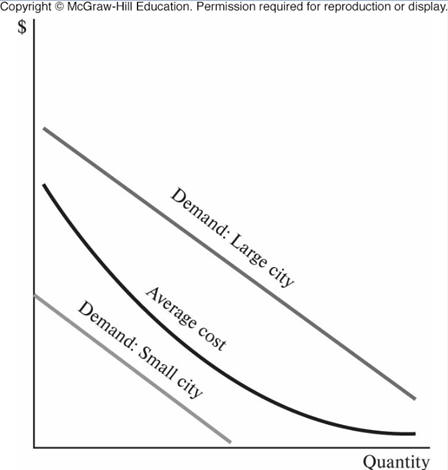
b. Differences between cities
Ex. - Museum exhibits, live music performances,
specialized retailers, medical procedures
.
.
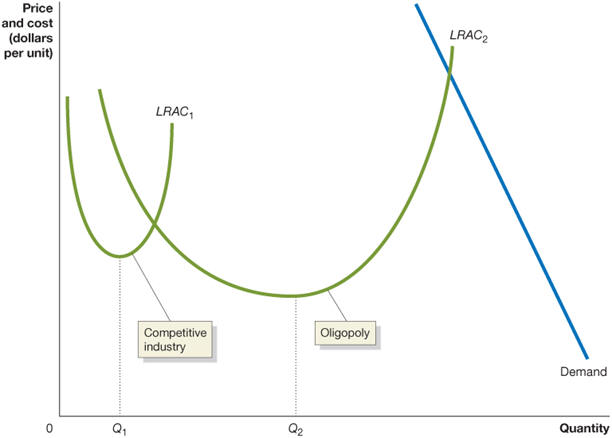
c. Differences across industries
- Scale economies large
relative to per capita demand => small
number of firms, large market areas
- Scale economies small
relative to per capita demand => large
number of firms, small market areas
.
.
3. Central Place Theory
a. Assumptions
(1) Fixed
population
(2)
Ubiquitous inputs - all inputs available at all locations
(3) Uniform demand - per-capita demand
is the same at all locations
(4) Perfect substitutes - no necessity
for comparison shopping
(5) No complementarity between goods -
single purpose shopping trips
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- Activities with the
same market areas will locate together -
shared parking, roads, and infrastructure
(economies of agglomeration)
- Central places result
when activities locate together
- Hierarchy develops
depending on number of services offered
.
b. Implications
- Diversity of city
sizes results because products have different
scale economies and different market areas
- Small number of
large cities, large number of small cities
- Customers travel to
bigger cities, not smaller or same size
cities
- Doesn't follow
exactly - some small areas contain higher
order goods, some large areas missing some
lower order goods
- Gives indication of
new business possibilities
.
c. Relaxing the assumptions
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
(1) Imperfect
substitutes
Ex. -
Clothes
.
(2) Complements
- People buy multiple goods on
the same shopping trip =>
complementary stores locate near one
another
Ex. - Restaurants, movie
theater
.
.
(3) Variation in demand
- Demand could be
higher or lower as city size increases
Ex. -
Country music, opera
.
(4) Resource-oriented
firms
Ex. - Saw mill
.
(5)
Local input-oriented firms
- Locate near cheap
labor, energy, intermediate goods
Ex. -
Research and development
.
.
|


