|
D. Greening the Economy
-
Is there a conflict between environmental
protection and economic growth?
-
Green economy
- an economy that improves human well-being and social equity, while
reducing environmental impacts (U.N.)
.
1. Relationship between the economy and
the environment
a. Impact of economic growth on the
environment
-
Environmental quality is a normal good -
people want more as income increases
-
Is it a luxury
good? - spending increases disproportionately as income rises
-
Environmental Kuznets Curve - environmental
impacts increase in early stages of economic development but
eventually decrease above some income level
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
-
Richer country uses more resources, demand
more energy, and produce more waste and pollution
-
Can also afford to invest in renewable
energy, install state-of-the-art pollution control equipment, and
implement environmental policies
-
Applies to some environmental impacts but
not all
Ex. -
Municipal solid waste, sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide
b. Impact of environmental protection on
the economy
-
Traditional view - environmental regulation
imposes additional costs to firms and reduces profits
-
Porter hypothesis
- environmental regulations motivate firms to identify cost-saving
innovations that otherwise would not have been implemented
-
Evidence is mixed, tends not to support the
Porter hypothesis at the national level
.
c. Decoupling
-
Separate increased economic activity and
increases in environmental impacts (bads)
-
Relative
decoupling - growth rate of environmental bad is positive but
less than the economic growth rate
-
Absolute
decoupling - environmental bad is either stable or decreasing
as the economy is growing
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
2. Evidence
a. Is environmental protection too
expensive?
.
b. Does environmental protection lead to
job losses?
.
c. Does environmental protection reduce
economic growth?
.
d. Does environmental protection harm
international competitiveness?
-
Some sectors negatively affected, others
positively affected
-
Regulations could lead to increased
productivity
3. Creating a green economy
a. Impact vs. business as usual
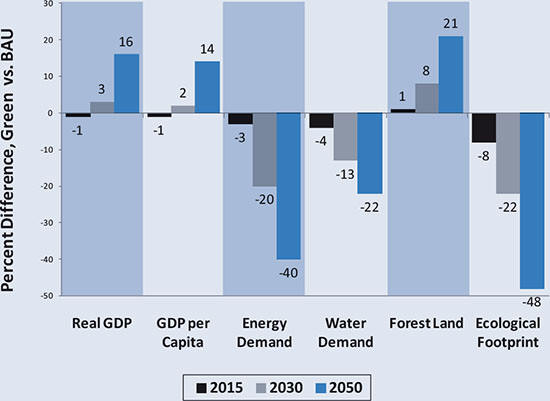
.
b. Policies
(1) Shift investments in infrastructure,
research, and development
(2) Use taxes and other market-based
instruments to internalize negative externalities
(3) Decrease government spending that
depletes natural capital
(4) Temporary support measures to ensure
employment transition for affected workers
(5) Strengthen international environmental
governance
.
|


