|
C. The Normal Distribution
1. Basic concepts
a. Continuous random variables
- results from a measuring process
- Can take on a
range of values
- Not possible
to calculate probability at a single
point
- Need to
calculate the probability of being in a
range
.
b. Continuous
probability density functions
Function such
that the area under the function between two
values is the probability of the random
variable taking on that value
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
2. Normal distribution
a. Properties
(1)
Bell-shaped and symmetric
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
(2) Measures
of central tendency are identical
(3)
Interquartile range is 1.33 standard
deviations
(4) Random
variable has infinite range
.
b. Standardizing
the normal distribution
Convert a normal
distribution with mean 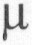 and
standard deviation and
standard deviation  into
a normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a
standard deviation of 1 into
a normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a
standard deviation of 1
X ~ N (μ,
σ)
Z ~ N ( 0 , 1 )
Ex. -
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
c. Standard normal
table
(1) Finding
probability, given values
(a) P(Z
< +)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
(b) P(Z
< -)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
(c) P(Z
> +)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
(d) P(Z
> -)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
(e) P(+
< Z < +)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
(f) P(-
< Z < -)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
(g) P(-
< Z < +)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
(2) Finding
values, given probability
=> X =
μ + Z σ
Ex. -
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
d. Excel
- =STANDARDIZE(X,
mean, standard deviation)
Gives Z value
.
.
- =NORMDIST(X,
mean, standard deviation, True)
P(X < X0)
.
.
Gives Z0, where P(Z < Z0) = prob
.
.
- =NORMINV(prob,
mean, standard deviation)
Gives X0, where P(X < X0) = prob
.
.
Six
Sigma Quality
|

