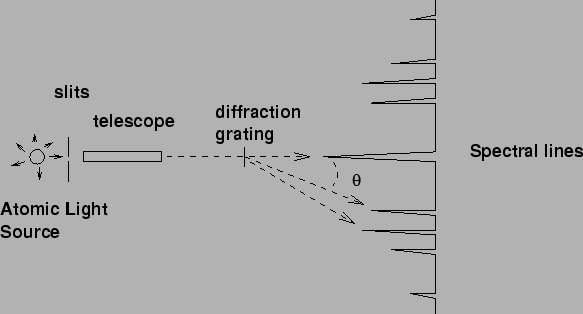

A series of colored bands of light is observed, indicating that the
glow coming from the light source is not a continuous distribution of
wavelengths, but rather a discrete spectrum of colors. It is the
interference effect that disperses light of differing wavelengths
through different angles. In addition, if one increases the observation
angle far enough, one can see that the pattern repeats. This repetition
is called the 2nd order spectra. In general,
the location of the Nth order maximum occurs at the angle ![]() such that
= N d, N = 1,2,3,....
where d is the separation between slits in the grating.
Thus the wavelength of radiation observed at a measured
angle
such that
= N d, N = 1,2,3,....
where d is the separation between slits in the grating.
Thus the wavelength of radiation observed at a measured
angle ![]() can be determined.
can be determined.
Various emitting sources are available. Determine the nature of 3 different spectra, and compare your results with the accepted values.