B. Trade-offs, Comparative Advantage, and the
Market System
- Scarcity - unlimited wants exceed the limited resources
available to fulfill those wants
1. Production possibilities frontier (PPF)
- Shows the maximum attainable combinations of two
products that may be produced with available resources and current
technology
Ex. - Missiles and wheat
| .................... |
M |
W |
| |
0 |
15 |
| |
1 |
14 |
| |
2 |
12 |
| |
3 |
9 |
| |
4 |
5 |
| |
5 |
0 |
.
.
.
- Opportunity cost -
highest value alternative that must be given up to engage in an
activity
Ex. - Cost of attending USD
.
.
.
- Increasing marginal opportunity costs
- Increasing the production of one good requires
larger and larger decreases in the production of the other
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- Economy produces increasing quantities of goods and
services
- Due to more resources or technological advances
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
2. The market system
a. Definitions
(1) Market
- Group of buyers and sellers of a good or service
and the institution or arrangement by which they come together for
trade
.
(2) Product markets
- Markets for goods and services
.
(3) Factor markets
- Market for inputs into the production process
.
(4) Factors of production
- Inputs used to make goods and services
.
(a) Labor
.
(b) Capital
.
(c) Natural resources
.
(d) Entrepreneurial ability
- Ability to bring together other factors of
production to produce and sell goods and services
.
b. Circular flow of income
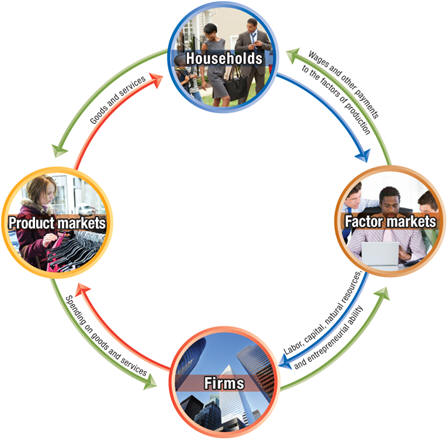
.
c. Market mechanism
- Adam Smith (1776) - An Inquiry into the Nature
and Causes of the Wealth of Nations
- Free market - few
government restrictions on economic activity
- Individuals act in a rational, self-interested way
- Prices send signals about the value of certain
products or activities => leads to the optimal allocation of resources
- Entrepreneurs -
operate businesses, bring together factors of production to produce
goods and services
.
d. Legal basis of market systems
(1) Protection of private property
- Market system requires property to be protected
from seizure by the government or by criminal elements
- Property rights -
rights individuals or firms have to the exclusive use of property,
including the right to buy or sell it
- Guaranteed by 5th and 14th amendments
- Protection of intellectual property
.
(a) Patents
- Protects new products or new ways to produce
products for a period of 20 years
.
(b) Copyrights
- Protects books, films, and software for a period
of 50 years after the death of the creator
.
(2) Enforcement of contracts and property rights
- Contracts must be carried out, private property
must be secure for market system to work
- Legal system used to have rights enforced
- Legal system must be independent from government
and outside forces
|


