
PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS
 |
| Fall 2020 |
 |
Economics 101 PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS |
|
|
|
|
The homework should be submitted as a picture via E-mail. It is due on Friday, October 16. No late homework will be accepted.
1. Suppose that workers in the United States can produce 40 computers or 20 tons of coffee in a particular period. Suppose workers in Brazil can produce 30 computers or 10 tons of coffee in the same period.
a. What is the opportunity cost for computers and for coffee in each country?
b. Which country has a comparative advantage in the production of computers, and which has a comparative advantage in the production of coffee?
c. Choose terms of trade that would make both countries better off.
.
2. Below is the market for kumquats in the United States both with free trade (without a quota) and with a quota
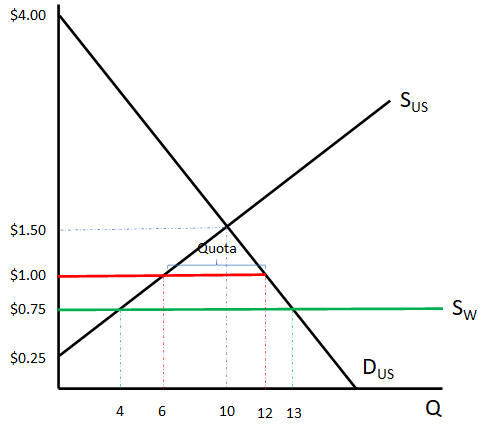
Calculate each of the values in the following table:
| Autarky (Without Trade) |
Free Trade (Without Quota) |
With Quota | |
| World Price of Kumquats | |||
| U.S. Price of Kumquats | |||
| Quantity Suppled by U.S. Firms | |||
| Quantity Demanded by U.S. Consumers | |||
| Quantity Imported | |||
| Consumer Surplus | |||
| Producer Surplus | |||
| Deadweight Loss |
For this question, you must show all work . If no work is shown, no credit will be given.
.
3. Suppose a person has $104 a month to spend on eating at high end restaurants (HE), casual dining (CD) restaurants such as California Pizza Kitchen and T.G.I. Fridays, and fast food (FF) restaurants. Going to the high end restaurants costs $32 each time, while the casual dining restaurants costs $16 each time and the fast food restaurants $8.
a. Suppose the table below shows the total utility associated with each level of consumption of the three products:
QHE 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 TUHE 0 192 352 480 576 640 672 QCD 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 TUCD 0 112 208 288 352 400 432 QFF 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 TUFF 0 80 152 216 272 320 360 Use the table to calculate the MU and MU / P for each possible quantity.
b. What is the utility maximizing combination of going to high end, casual dining, and fast food restaurants for this consumer? Show that the condition for utility maximization is met.
.
Extra Credit: Who won the 2020 Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences, and why were they given the award?