



Next: Questions:
Up: Current and Voltage Measurements
Previous: Introduction:
Contents
Each lab team will be provided with 3 500 resistors, and a light
bulb. A spool of hook-up wire and a spool of nichrome wire will be
available to all teams as well. The measuring circuit will consist of
a power supply, an ammeter, a voltmeter, and a resistance to be tested
called the RUT (resistance
under test). The ammeter will be placed in series with the power supply
and the RUT so that the ammeter can measure the current 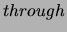 the
RUT (and everything in series with it).
The voltmeter will be in parallel with the RUT.so that it can measure
the potential difference between the terminals of the RUT. The ammeter
measures current flow at a point in a circuit. The voltmeter measures the
difference in potential
between two points points in a circuit. For each RUT, vary the voltage
of the power supply and measure
the
RUT (and everything in series with it).
The voltmeter will be in parallel with the RUT.so that it can measure
the potential difference between the terminals of the RUT. The ammeter
measures current flow at a point in a circuit. The voltmeter measures the
difference in potential
between two points points in a circuit. For each RUT, vary the voltage
of the power supply and measure 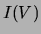 . Record the data in a table.
The RUT will be in turn a
. Record the data in a table.
The RUT will be in turn a
- 500 resistor,
- 3 500 resistors in series,
- 3 500 resistors in parallel,
- a light bulb (do NOT crank the voltage past ``7'',
- a spool of hook-up wire, and
- a spool of nichrome wire.
Compare the slope of the 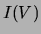 graph for the 500 resistor with
the value encoded on its body (using the color bands). Compare uncertainty
with discrepancy.
For the wire in the spools, measure the diameter and estimate the length.
From your measurement of the slope of the
graph for the 500 resistor with
the value encoded on its body (using the color bands). Compare uncertainty
with discrepancy.
For the wire in the spools, measure the diameter and estimate the length.
From your measurement of the slope of the 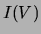 graph, estimate
the resistivity of the two substances. Compare your results with
the expected value for the case of nichrome; for the hook-up wire,
guess what the substance might be.
graph, estimate
the resistivity of the two substances. Compare your results with
the expected value for the case of nichrome; for the hook-up wire,
guess what the substance might be.




Next: Questions:
Up: Current and Voltage Measurements
Previous: Introduction:
Contents
greg severn
2000-10-24